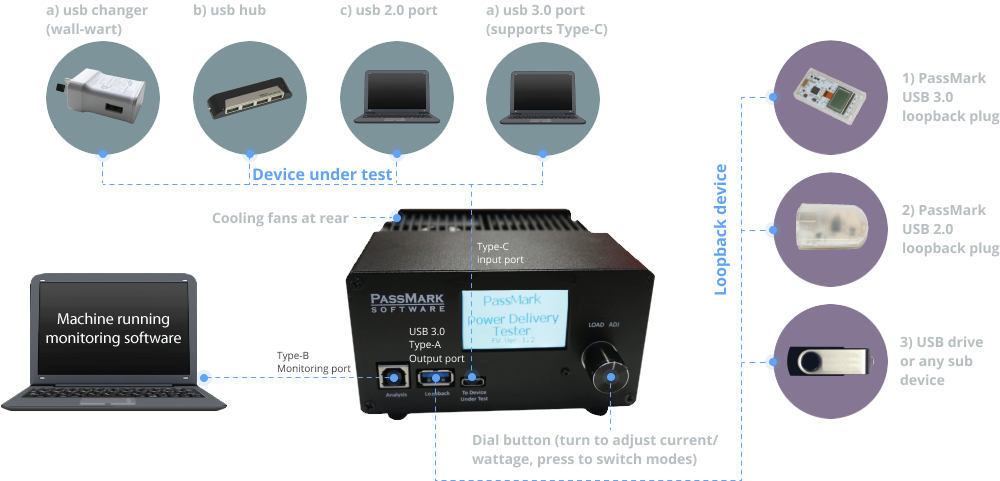
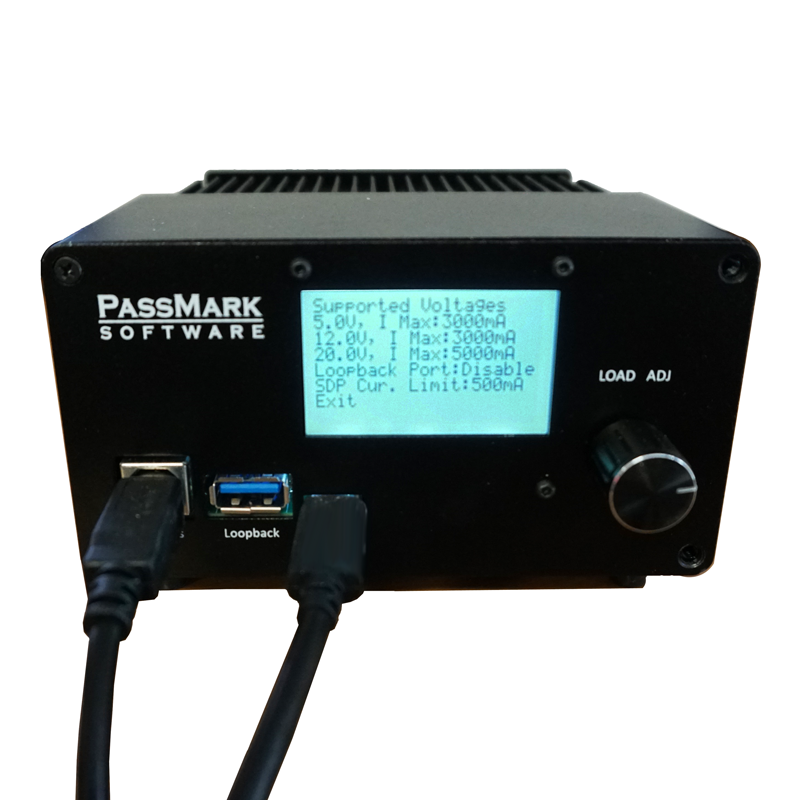
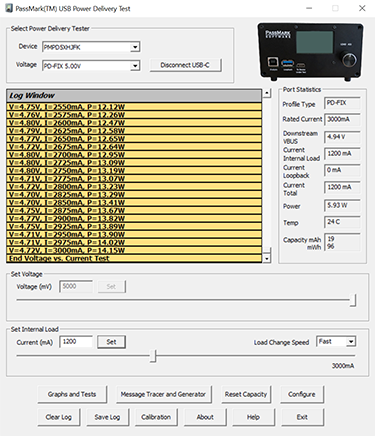
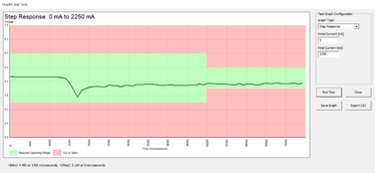
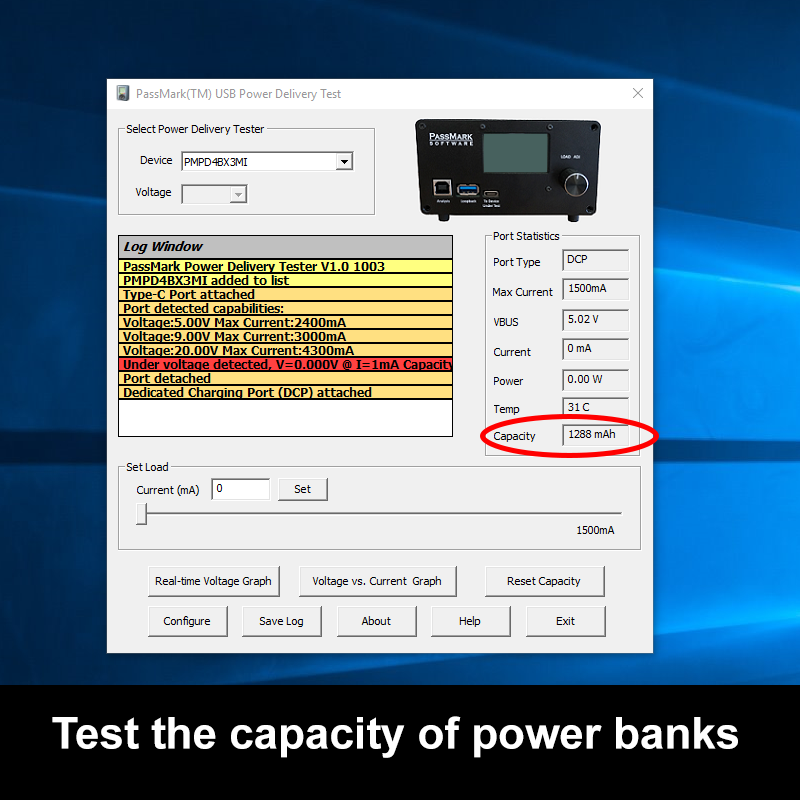
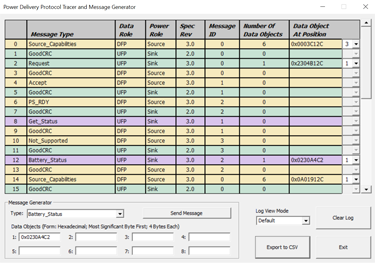
Tests the power delivery capability of USB ports up to 100Watts according to USB Battery Charging 1.2 and USB Power Delivery standards.
Tests the power delivery capability of USB chargers (Detects proprietary chargers and adjusts the maximum current accordingly).
Negotiates voltage levels with host PD controller chip to switch between different voltage levels. Dissipates 50 watts continuously, and up to 100 watts for short periods.
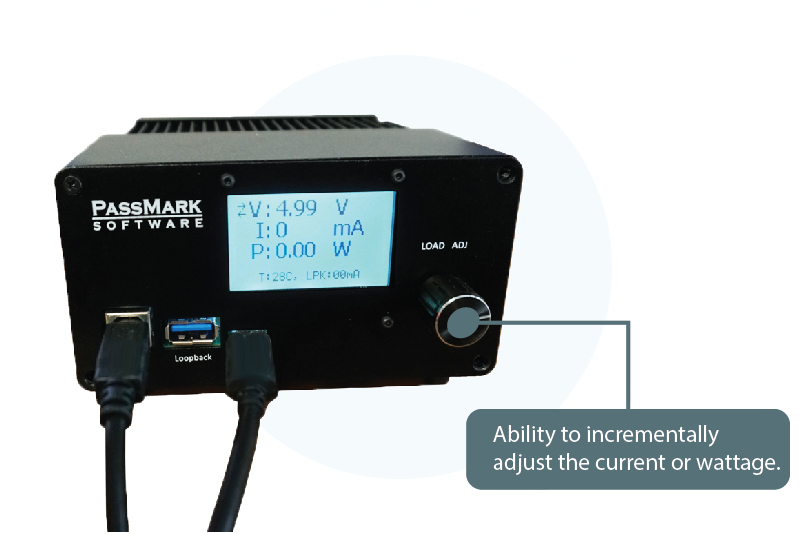
Current can be adjusted with milliamp precision using rotary encoder or via software.